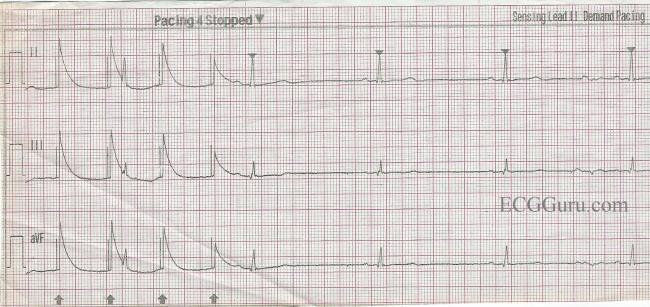
√100以上 sinus bradycardia with pacer spikes 975862
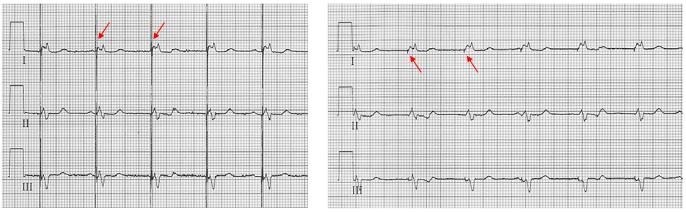
Function Single chamber atrial pacemakers are uncommonly placed, as they require intact atrioventricular conduction and do9/3/16Name this strip A Normal Sinus Rhythm with Unifocal Couplet PVC'S B Normal Sinus Rhythm with Multifocal PVC'S C Normal Sinus Rhythm with Pacer Spikes D Sinus Bradycardia3 seconds Patients with a congenital heart disorder and impaired hemodynamics due to sinus bradycardia
Transcutaneous Pacing Tcp The Problem Of False Capture Ems 12 Lead
Sinus bradycardia with pacer spikes
Sinus bradycardia with pacer spikes-The pacer was programed to VVI mode and AAI mode and ECG recordings were made This is a rhythm strip recorded from a man attending the pacemaker followup clinic The Patient had been implanted with a ventricular pacemaker one week before In about the middle of the tracing a magnet was placed over the pacemaker15/5/21Atrial rhythms originate in the atria rather than in the sa node The top countries of supplier is china, from which the percentage Normal ekg rhythms include a normal sinus rhythm in which each p wave is followed by a qrs complex and occur at a rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute Pacer spikes can be seen in lead i



Http Www Gwicu Com Assets Nursing protocols 18 pacer temporary dual chamber pacer medtronic 5392 hints Pdf
Bradycardia occurs when electrical signals slow down or are blocked Sinus node problems Bradycardia often starts in the sinus node A slow heart rate might occur because the sinus node Discharges electrical impulses slower than isProgression to myocardial depression and cardiogenic shock sinus node dysfunction (most common reason), Atrial pacemaker normal rhythm is easy to identify with pacer spike preceding a narrow QRSAppropriate cable 2 Turn Pacer modality on 3Press start 4Increase mA until you have a pacer spike, followed by a QRS associated with a pulse Special multifunction pad cable is inserted here Remember to plug sync cable or ECG leads into Defib machine
For instance, if there were inappropriate sinus bradycardia at less than 60 bpm, the atrial pacer would take over if it is programmed to wait 1 second before firing (The atrial pacer would also fire if it failed to sense the atrial activity)Atrial (Pwave) Not sensed = Trigger pacer fires an atrial spike If AV conduction is normal If QRS is sensed = Inhibition ( V pacer spike does not fire ) If QRS is NOT sensed ( absent or delayed) = Trigger pacer fires a ventricular spike An upper rate is set for the ventricular response to avoid track ing rapid atrial activity ( Menu 2)12/1/21This type of pacing is commonly used only for atrial pacing in sinus bradycardia, supraventricular tachycardia or for diagnostic studies atrial pacing &
Sinus bradycardia ECG, causes &14/6/17Sinus bradycardia occurs on an ECG when there is a normal upright P wave in lead II ― sinus P wave ― preceding every QRS complex with aPacemaker mediated tachycardia on ECG Pacemaker beats are mostly easy to recognize on the ECG Pacemaker stimulation generates a stimulation artifact ("pacemaker spike") Older pacemakers generate large and clearly visible spikes, whereas newer models may generate very minute or even invisible spikes (at least in some leads)



Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationidentifying Complete Heart Block And The Use Of Temporary Cardiac Pacing In The Emergency Department Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education



Transcutaneous Pacing Tcp The Problem Of False Capture Ems 12 Lead
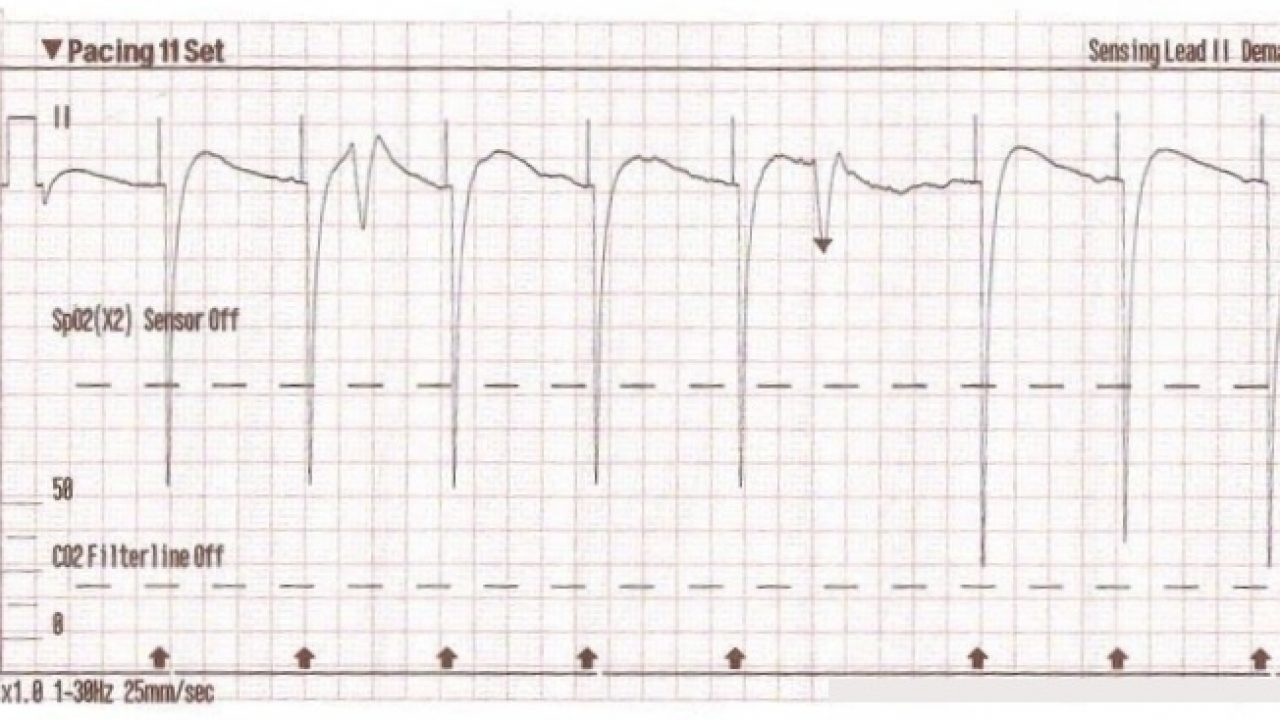
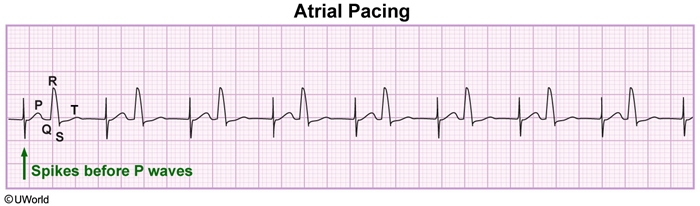
4/6/21The appearance of the ECG in a paced patient is dependent on the pacing mode used, placement of pacing leads, device pacing thresholds, and the presence of native electrical activity Features of the paced ECG are Pacing spikes Vertical spikes of short duration, usually 2 ms May be difficult to see in all leads26/4/18You should have a pacer spike, (AAI) for sinus bradycardia or alternatively for rapid atrial overdrive pacing of supraventricular tachycardia, (SVT) and atrial flutter Rarely used, higher output requirements, patient discomfort Stay tuned for part 4!A 12lead ECG was obtained as shown below This was interpreted as sinus bradycardia, with a narrow QRS complex and significant Twaves abnormalities There did not appear to be any STsegment or Twave changes concerning for ischemia The large voltages recorded on the rightside of the strip occurred when the transcutaneous pacer was restarted



Q Tbn And9gcqcs9jthjglzze9aobv 46n5d36czj99jj6hhe8hyng Gowr1zk Usqp Cau




19 The Basis Of Ecg Diagnosis
15/4/05Physiologic sinus bradycardia, which can occur in highly trained athletes, must be excluded and should not be confused with pathologic bradyarrhythmias ACC/AHA/NASPE Recommendations1/7/2111 Sinus Node Dysfunction Sinus bradycardia, sinus pause or arrest, or sinoatrial block, chronotropic incompetence Often 98 Examples of Rhythms Noncapture Pacer stimulus fails to cause myocardial depolarization Pacer spike is present but no ECG waveform Fires but fails to capture Undersensing Fails to sense ECG Pacer spikesICU) ≥ 125/min Ventricular tachycardia




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog Extreme Bradycardia A Case Based Lesson In Pacing




Pacemakers Cancer Therapy Advisor
Si tienes bradicardia, el cerebro y otros órganos podrían no recibir suficiente oxígeno, lo que posiblemente provoque estos síntomas Desvanecimiento o desmayo (síncope) Mareos o aturdimiento Fatiga Dificultad para respirar Dolores en elSingle chamber cardiac pacemakers are cardiac conduction devices with one lead terminating in (most commonly) the right ventricular apex or the right atrium Components Includes one of the following lead in the right atrium lead in the right ventricle;12/2/07Sinus bradycardia (as an alternative to pharmacologic treatment) To restore AV mechanical synchrony in underlying third degree block, The larger current in a unipolar system creates much larger pacing spikes on the surface ECG Figure 1 Open in figure viewer PowerPoint Unipolar epicardial pacing electrodes




Bradycardia Emcrit Project



Transcutaneous Pacing Tcp The Problem Of False Capture Ems 12 Lead
27/4/21Sinus bradycardia caused by either heart block or sinus node dysfunction that is not reversible and is producing symptoms may be treated with a permanent pacemaker In some cases, such as partial AV block caused by a myocardial infarction (heart attack), a trial of a temporary pacemaker may be done to determine if the AV block is permanent or reversibleAsymptomatic sinus bradycardia in children with a complex congenital heart disorder and resting heart rate of <Sinus arrest or AV block;




Pdf Temporary Transvenous Pacemaker Placement In The Emergency Department




Pacemakers And Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators Ppt Video Online Download
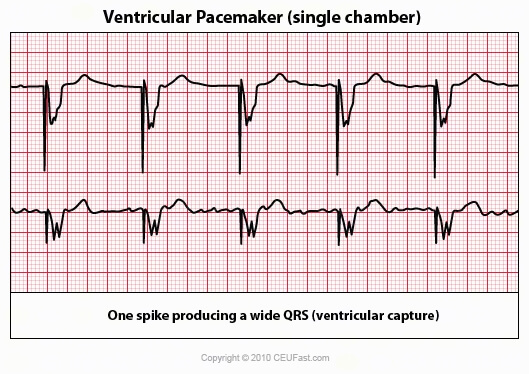
1/5/18If rate is ~70, consider pacemaker rhythm search for pacer spikes <26/9/19Sinus bradycardia is a slow, regular heartbeat It happens when your heart's pacemaker, the sinus node, generates heartbeats less than 60 times in a minute For some people, such as healthy youngExit Block typically results in presence of pacer spikes but no resultant P or QRS depolarization This is caused from injury or process that affects the endocardium at site of pacer electrode Most often this is from an MI that causes injury at this electrode site causing scarring that prohibits conduction of the pacer spike




Ekg Artificial Pacemakers Tachycardia Bradycardia Leveluprn



Pitfalls And Pearls Of Temporary Transvenous Cardiac Pacing Resus Review
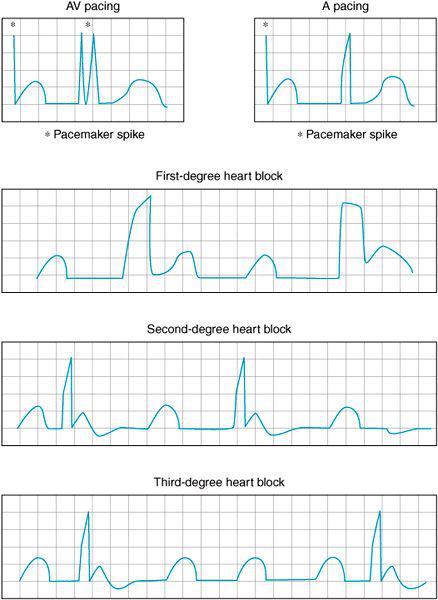
40 beats/minute or pauses in ventricular rate of >22/3/Bradycardia and hypotension are most common initially —>14/7/10Pacemaker Configurations AAI Indications Sick sinus syndrome in the absence of AV node disease or atrial fibrillation 14 Pacemaker Configurations VDD Indications AV block with intact sinus node function (particularly useful in congenital AV block) 15 Pacemaker Configurations DDD Indications 1 The combination of AV block and SSS 2




Temporary Epicardial Pacing After Cardiac Surgery A Practical Review Reade 07 Anaesthesia Wiley Online Library




Ekg Ecg Interpretation Course Ceufast Nursing Continuing Education
Sinus rhythm with multifocal premature ventricular contraction (PVC) couplet Sinus Rhythm with PACs Sinus Bradycardia with Pacer Spikes Sinus Bradycardia with Escape Beats Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Ventricular fibrillation (Vfib) Ventricular tachycardia (Vtach)Sinus node dysfunction with failure of the SA node to generate an appropriate heart rate response Persistent bradycardia despite oxygen administration, breathing and chronotropic drug administration (Hazinski, 12) Junctional and ventricular escape rhythms Advanced AV block Congenital or acquired heart disease601/min accelerated idioventricular rhythm (reperfusion arrhythmia;



Implantable Cardiac Devices Clinical Gate



1
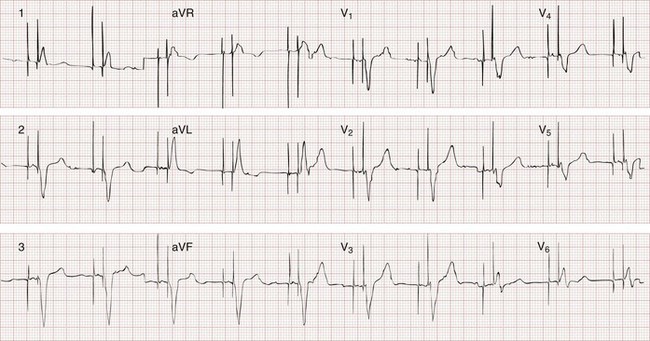
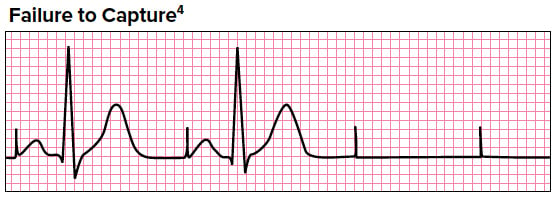
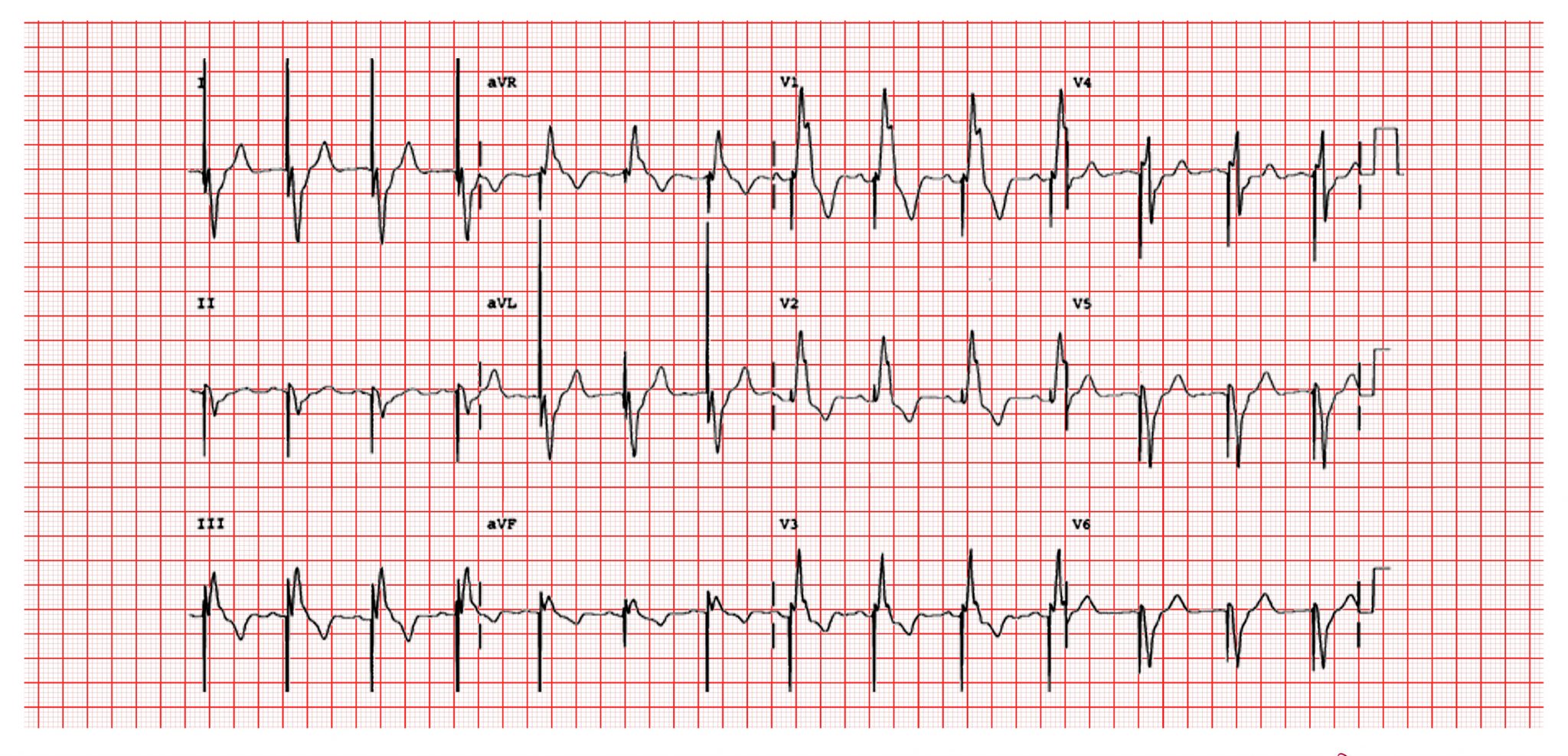
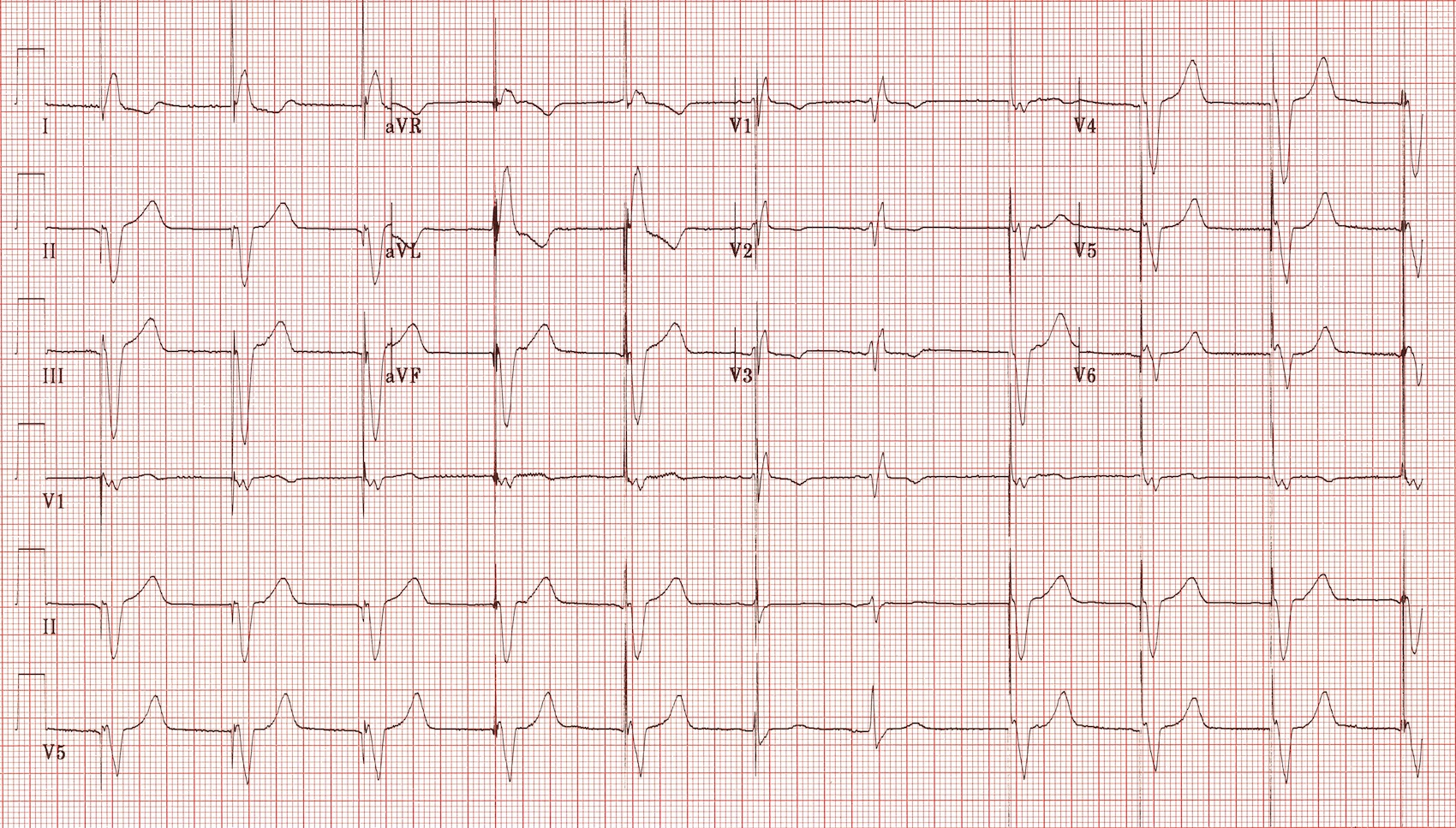
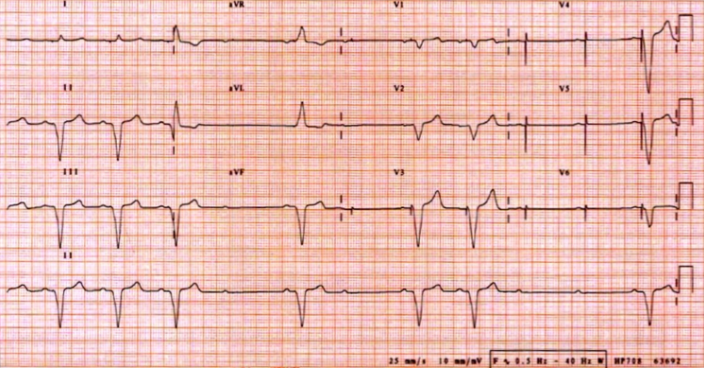
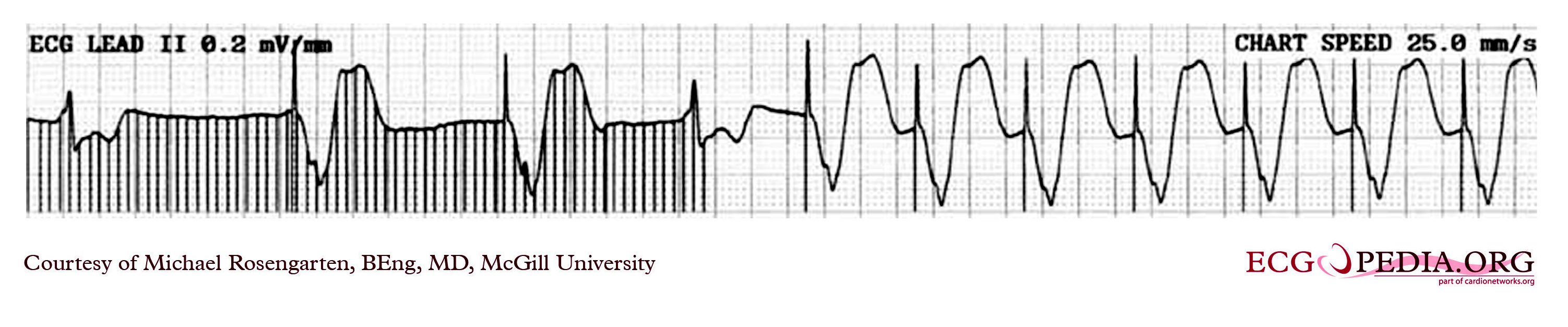
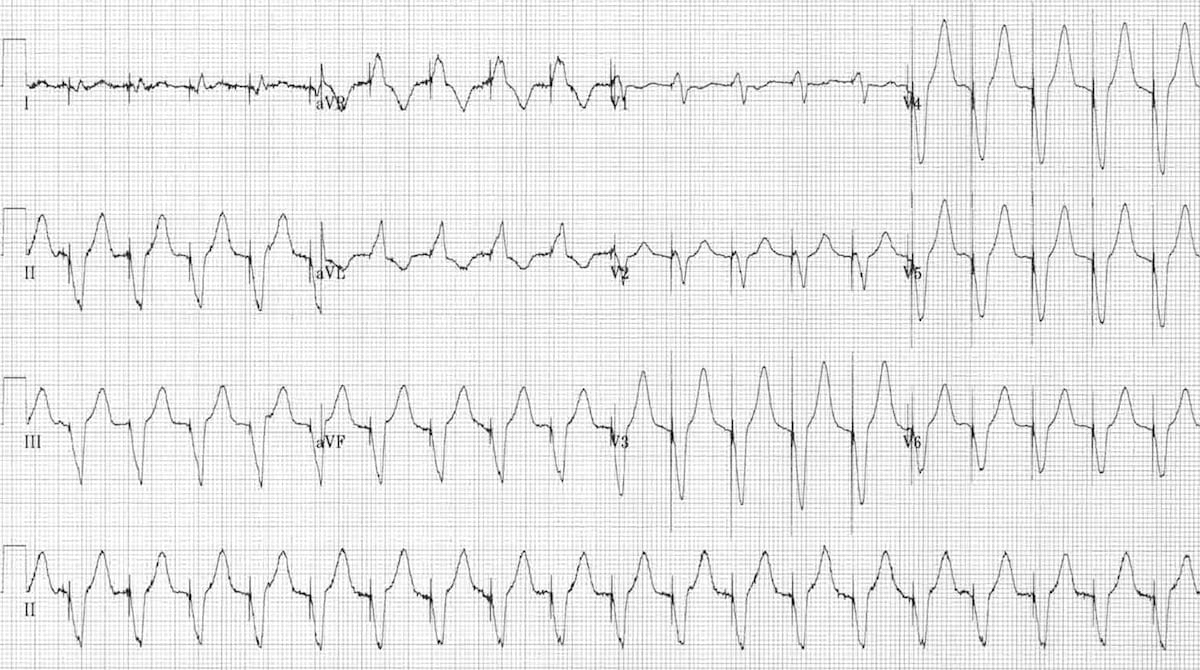
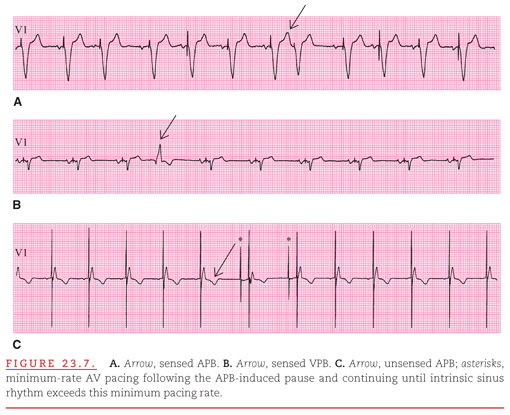
Sinus Bradycardia 5 Regular Rate 80 P waves inverted before QRS PRI 008 (006, 008, 010 acceptable) Pacer spikes are before the P wave and before the QRS, so trying to pace the atria and the ventricles For each pacer spike, you see an appropriate complex27/4/14The pacer spikes, for the most part, track the P waves, which is how this pacemaker is programmed They are not followed by a paced QRS complex, however This is failure to capture The second and fourth P waves did not stimulate a pacer spike because of their proximity to the T wave of the junctional beatFigure 2 A 12Lead EKG showing sinus bradycardia Pacer spikes are present, and demonstrate an inability to both capture and to sense intrinsic ventricular activity (arrows) Figure 3 Chest XRay demonstrates a singlelead permanent pacemaker with a complete transection of its lead inferior to the clavicle at the level of the first rib (arrow)



Pacemaker Basics For The Emergency Physician Emra




Ekg Strips Flashcards Quizlet
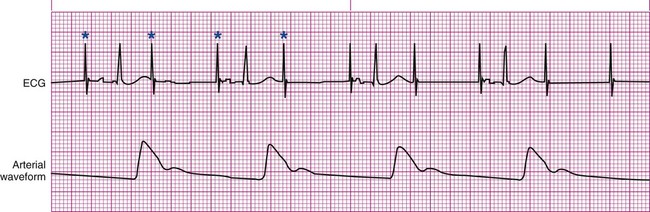
Once the pacer spikes are identified, the heart rate cannot be lowered any further Betablockers can be given for shortterm use, such as for a CT study, in patients with diabetes, psoriasis, controlled congestive heart failure, and ablated WolffParkinsonWhite syndromeCapture occur after pacer spikes 1,3,5, and 7 The remaining pacer spikes fail to capture, resulting in no conduction to the ventricles, and no arterial waveform)60/min ventricular escape (usually 3540/min) – why?



Pacemakers A Beginner S Guide Geeky Medics



Pacemakers Basic Advanced Concepts Core Em
30/7/12Sinus bradycardia with atrial ectopy b Normal sinus rhythm with bigeminal PVCs c Sinus tachycardia with frequent multifocal PVCs Atrial pacer spikes precede each P wave 10 c Sinus rhythm with trigeminal PJCs No P waves are associated with the ectopic beats18/9/19Sinus bradycardia is a type of sinus arrhythmia in which your heart is beating slower than usual Normally, your heart requires a specialized group of cells to initiate the signal and produce a beat These cells are located in the sinoatrial node, which is firing the signals at a speed of 60 to 100 times per minute25/6/16Sinus bradycardia with a sinus pause The rhythm is irregular The heart rate is 40/min The P waves have a corresponding QRS complex and are positive There is a 2 sec pause that follows the 1st complex No ectopic beats are seen PR sec, QRS 08 sec QT 40 sec Interpretation Sinus bradycardia with a sinus pause



Transcutaneous Pacemaker Failure To Capture And False Qrs Artifact Ecg Guru Instructor Resources



Perioperative Rhythm Abnormalities Anesthesia Key
28/4/21Sinus bradycardia is the same as NSR, but the HR is <60bpm If the lead is in the right atria, the rhythm will appear like NSR but with a pacer spike before the P wave If the lead is in the right ventricle, it will look like a slow VTACH with a pacer spike before the QRSSinus bradycardia to a heart rate of 30 Her bradycardia was treated successfully with intravenous atropine unit for temporary transvenous pacer placement as well as antibiotic treatment Discussion Carotid sinus syndrome presents with episodes of syncope and1/12/1981The amnesia occurred during a period of hypotension secondary to sinus bradycardia The amnesia recurred in absence of bradycardia and hypotension The temporal lobe spiking lends credence to the thought that transient global amnesia occurs as the result of seizure activity



Http Www Gwicu Com Assets Nursing protocols 18 pacer temporary dual chamber pacer medtronic 5392 hints Pdf



Q Tbn And9gcsztx Yiup6dgjcscknsguogls0mjbhalqbp1auz2 K1yzjb3ef Usqp Cau
13/6/17Wandering atrial pacemaker is similar to multifocal atrial tachycardiaexcept the heart rate is normal ― that is, less than 100 beats per minuteThe differential diagnosis for broad complex tachycardia with pacing spikes are pacemaker mediated tachycardia or runaway pacemaker syndrome Development of atrial fibrillation or flutter in patients with a dual chamber pacemaker (in the setting of complete heart block) leads to pacemaker mediated tachycardiaSinus bradycardia with a PJC 4 a Normal sinus rhythm with multiform PVCs b Normal sinus rhythm with unifocal PVCs There are ventricular pacer spikes for each of the QRS complexes but the atrial pacer spikes are not always present 3 Normal sinus rhythm with a PJC b Normal sinus rhythm with a PJC



Jts Amedd Army Mil Assets Docs Cpgs Critical Care Air Transport Cpgs Transcutaneous Temporary Transvenous Pacing Ccat 30 Jan Pdf



The Basics Of Paced Rhythms Ecg Medical Training
Normal Sinus Rhythm with Unifocal Couplet PVC'S Normal Sinus Rhythm with Multifocal PVC'S Normal Sinus Rhythm with Pacer Spikes Sinus Bradycardia with PVC'SManagement Definition of sinus bradycardia Sinus bradycardia fulfills the criteria for sinus rhythm but the heart rate is slower than 50 beats per minute ECG criteria follows Regular rhythm with ventricular rate slower than 50 beats per minute Pwaves with constant morphology preceding every QRS complexSinus bradycardia is a type of slow heartbeat A special group of cells begin the signal to start your heartbeat These cells are in the sinoatrial (SA) node Normally, the SA node fires the signal at about 60 to 100 times per minute at rest In sinus bradycardia, the node fires less than 60



Pacing



Pacemaker Rhythms Normal Patterns Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



Ekg Ecg Interpretation Course Ceufast Nursing Continuing Education



Pacemaker Basics For The Emergency Physician Emra




Pacing Spikes Following Qrs Complexes What Is The Mechanism Zabek 19 Annals Of Noninvasive Electrocardiology Wiley Online Library



Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationecg Pointers Pacemakers And When They Malfunction Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education




Pacemakers And Defibrillators Flashcards Quizlet



Cardiovascular Therapeutic Management Nurse Key




Pacemaker Review Rush Emergency Medicine



Transcutaneous Pacing Tcp With And Without Capture Acls Medical Training




Evaluation Of Bradycardia In The Emergency Department 17 09 06 Ahc Media Continuing Medical Education Publishing




The Ekg In A Patient With A Pacemaker Wikidoc




Electrocardiographic Troubleshooting Of Implanted Cardiac Electronic Devices Intechopen



Pacemakers Basic Advanced Concepts Core Em




Cardiac Pacing And Defibrillation Dr Fadhl Alakwaa Fadlworkgmail



The Ekg In A Patient With A Pacemaker Wikidoc



Pitfalls And Pearls Of Temporary Transvenous Cardiac Pacing Resus Review



Www Capefearvalley Com Careersx Documents ka Studyguide Pdf




Pacemakers Basic Advanced Concepts Core Em




Electrocardiographic Troubleshooting Of Implanted Cardiac Electronic Devices Intechopen




Pacemakers And Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators Cardiac Rhythm Disturbances Clinical Electrocardiography A Simplified Approach 7th Edition 06



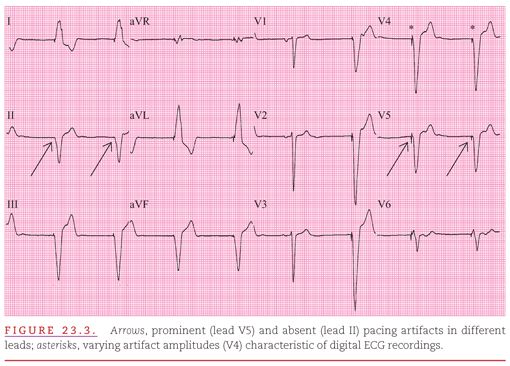
Pacemaker Malfunction Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



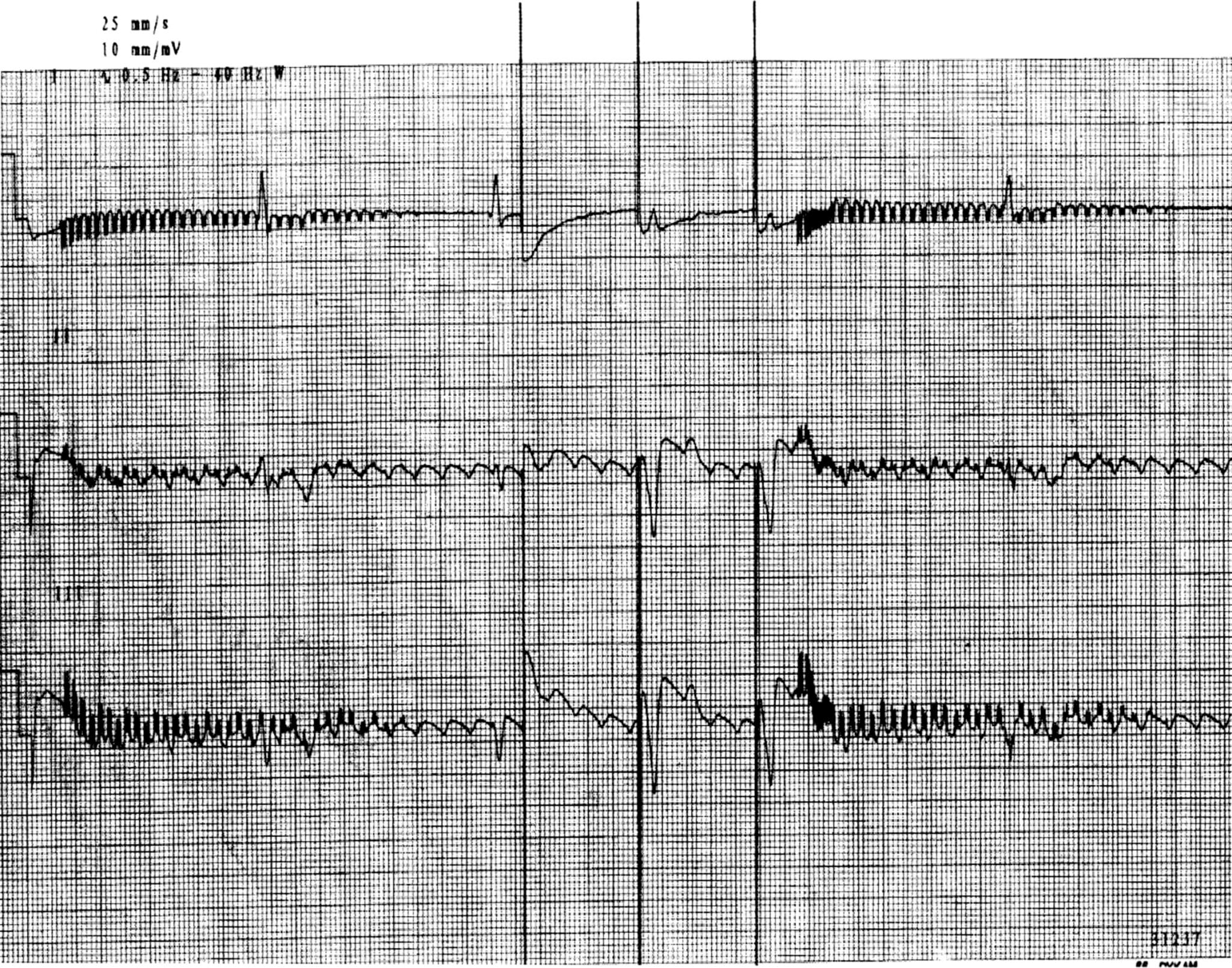
Artificial Cardiac Pacemakers Thoracic Key



Pacemaker Basics Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog




Pacemaker Review Rush Emergency Medicine




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog Extreme Bradycardia A Case Based Lesson In Pacing
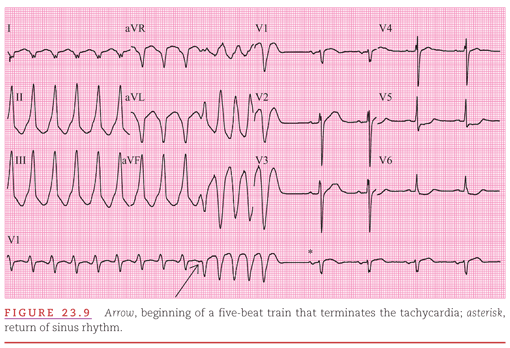



Artificial Cardiac Pacemakers Thoracic Key




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog Extreme Bradycardia A Case Based Lesson In Pacing
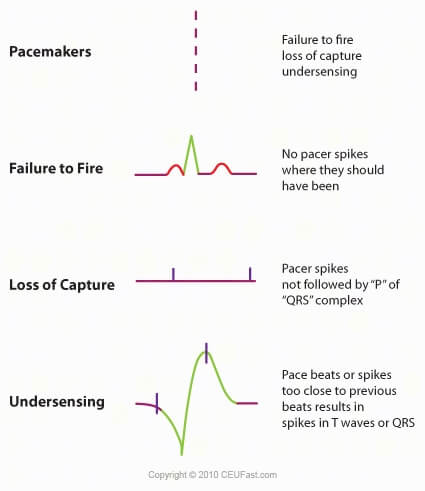



Ekg Ecg Interpretation Course Ceufast Nursing Continuing Education



Transcutaneous Pacing Tcp The Problem Of False Capture Ems 12 Lead
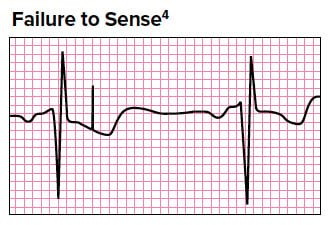



Pacemaker Basics For The Emergency Physician Emra



The Ekg In A Patient With A Pacemaker Wikidoc
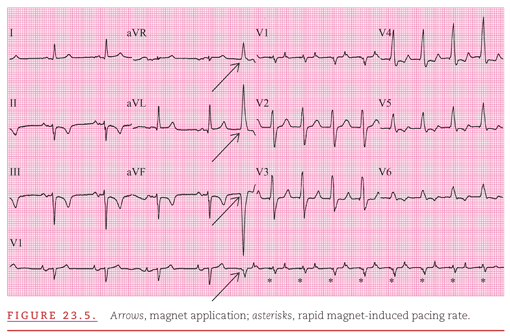



Artificial Cardiac Pacemakers Thoracic Key



Transcutaneous Pacing Tcp The Problem Of False Capture Ems 12 Lead



Artificial Cardiac Pacemakers Thoracic Key



Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationecg Pointers Pacemakers And When They Malfunction Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education




Cardiac Pacing And Defibrillation Chapter 10 Core Topics In Cardiothoracic Critical Care



Ecg Abnormalities Almostadoctor



Utmc Utoledo Edu Depts Nursing Pdfs Advanced ekg refresher Pdf



Devices Textbook Of Cardiology



Cardiac Ecgs Flashcards Memorang




Electrophysiology Of The Heart Ecg Monitoring The Ecg




How To Recognize Treat Heart Block Jems




An Overview Of Permanent Cardiac Pacing
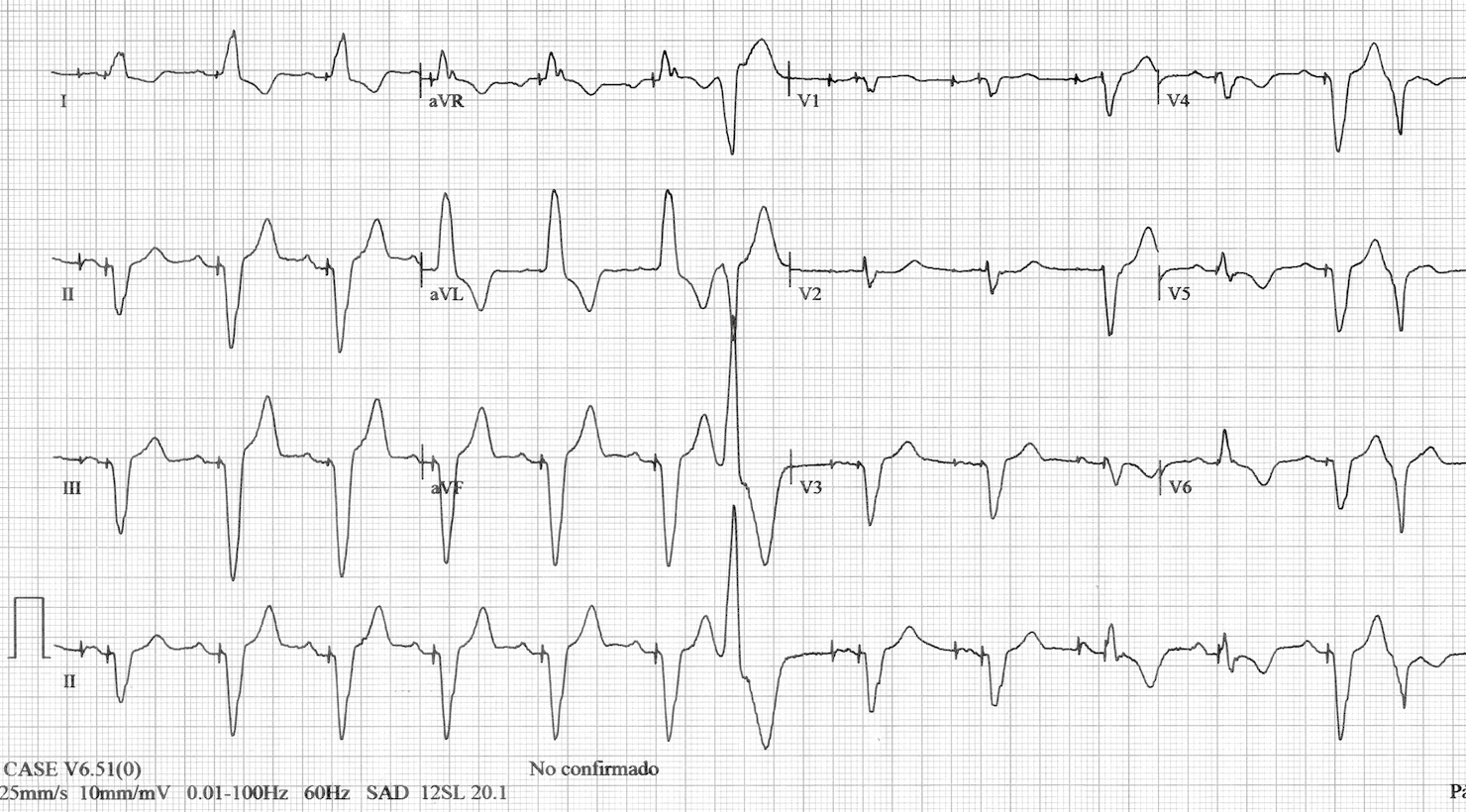



Different Qrs Morphologies In A Dual Chamber Pacemaker What Is The Mechanism Gutierrez Journal Of Thoracic Disease



The Basics Of Paced Rhythms Ecg Medical Training
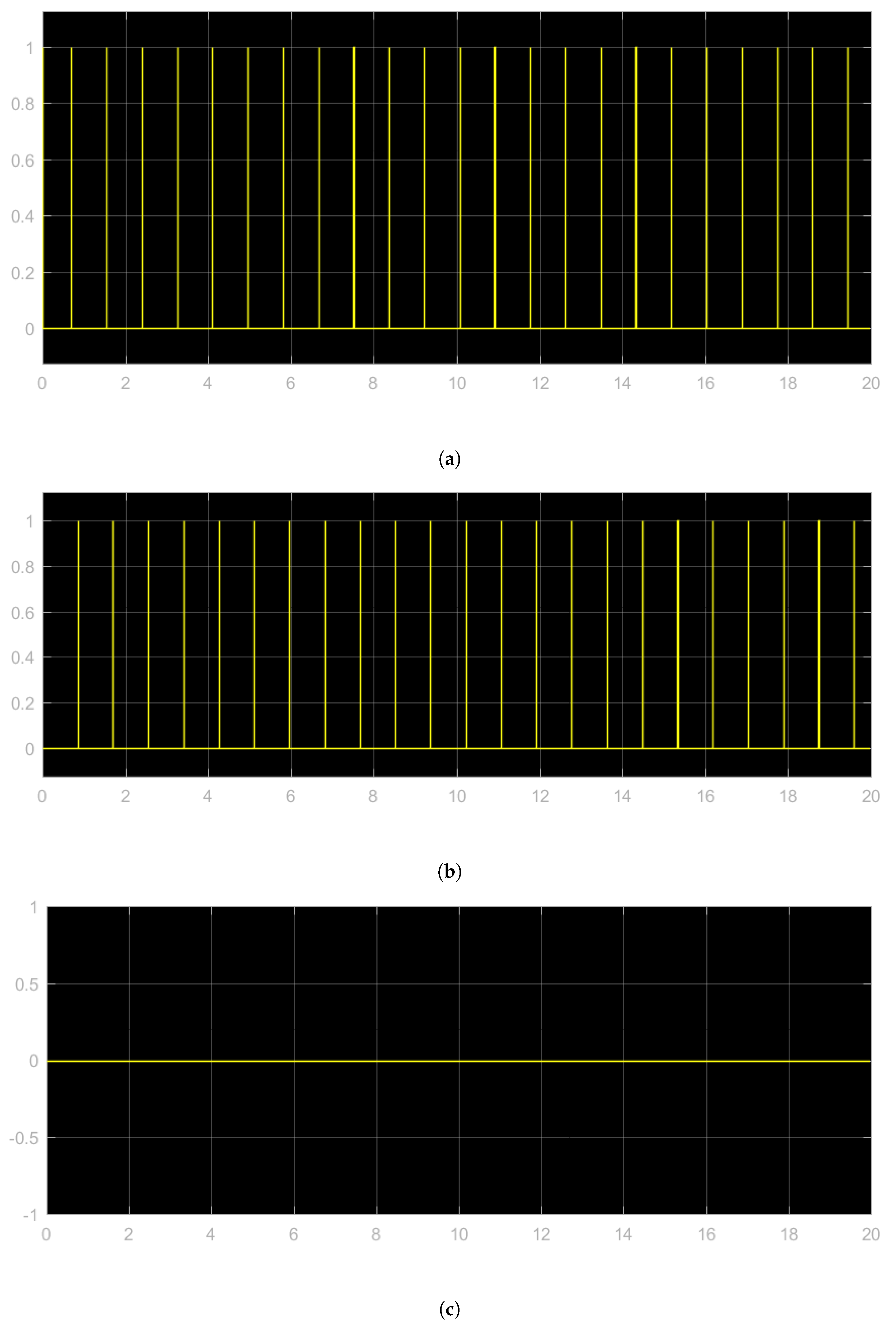



Electronics Free Full Text Hardware In The Loop Implementation Of The Oscillator Based Heart Model A Framework For Testing Medical Devices Html



Pacing



Heart Rhythm Guide



The Basics Of Paced Rhythms Ecg Medical Training



Http Www Gwicu Com Assets Nursing protocols 18 pacer temporary dual chamber pacer medtronic 5392 hints Pdf



Utmc Utoledo Edu Depts Nursing Pdfs Advanced ekg refresher Pdf




Ecg After Placing A Temporary Pacemaker Showing Sinus Bradycardia And Download Scientific Diagram




12 Lead Ecg Demonstrating Ventricular Paced Rhythm Note The Download Scientific Diagram
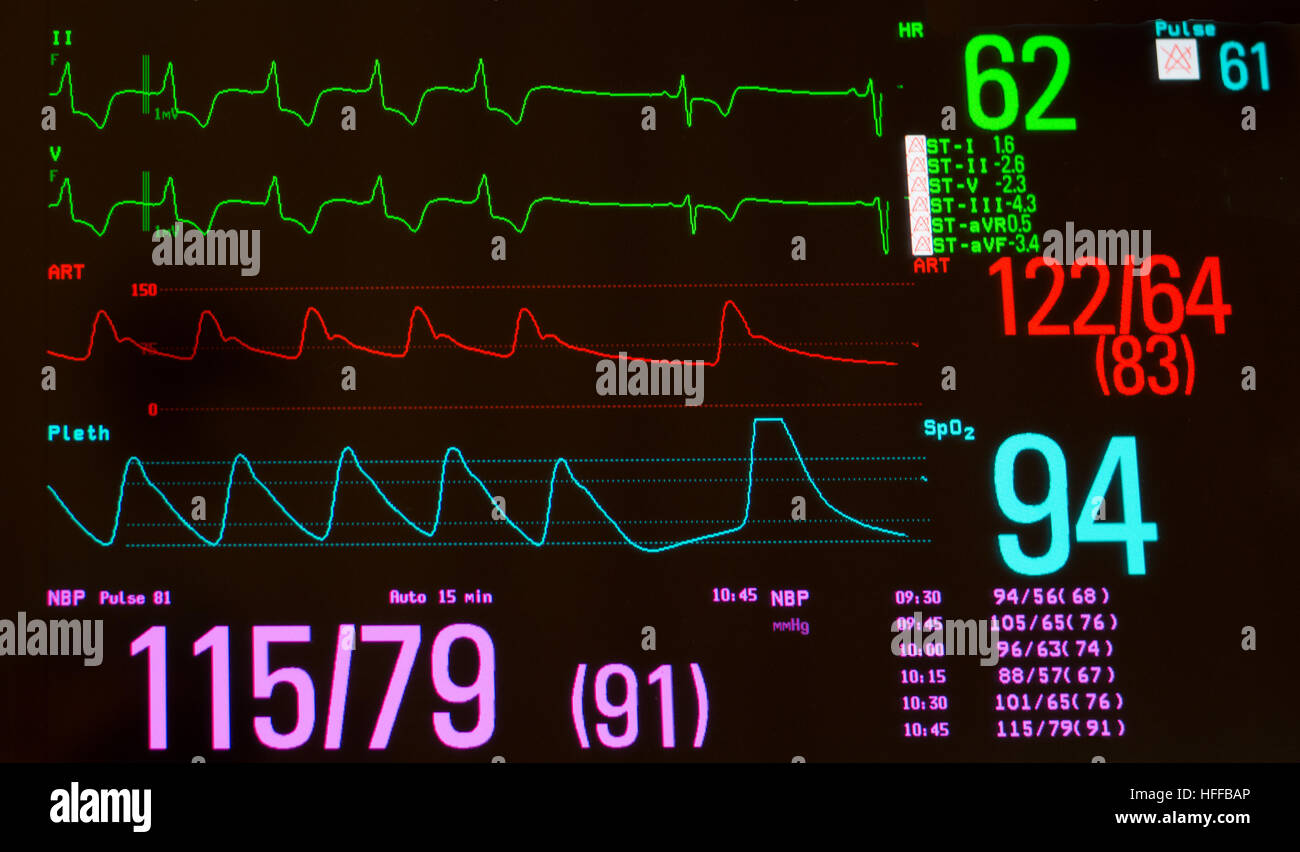



Monitor With Paced Heart Rhythm To Sinus Bradycardia Arterial Blood Pressure Oxygen Saturation And Noninvasive Blood Pressure Stock Photo Alamy



Emergency Medicine News
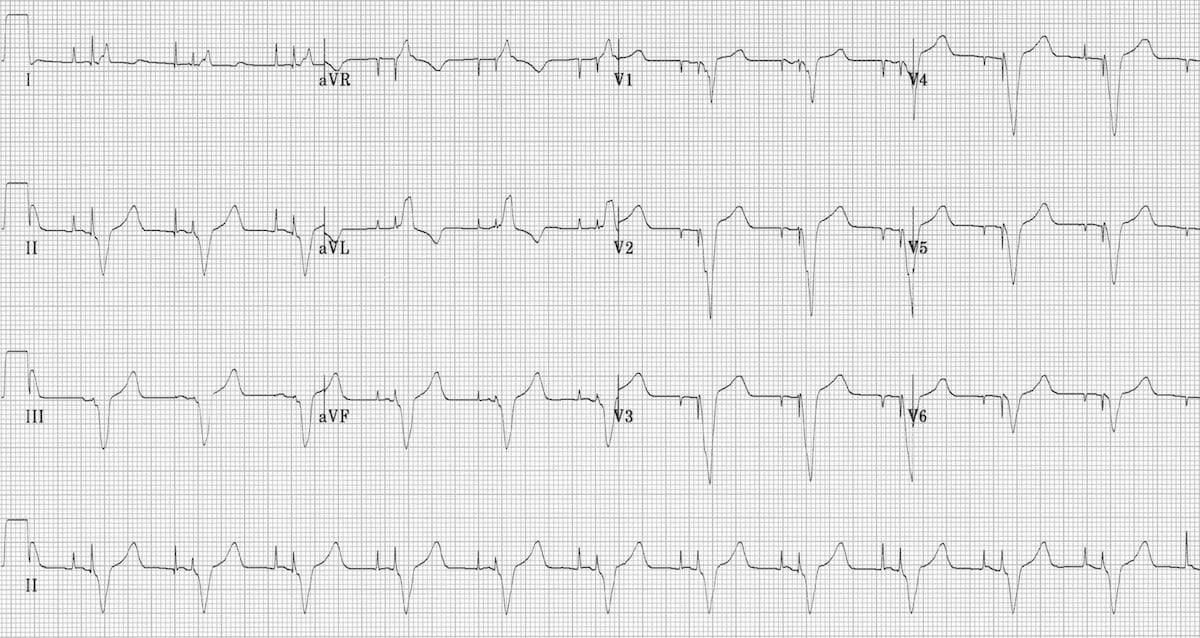



Pacemaker Rhythms Normal Patterns Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Electrocardiographic Troubleshooting Of Implanted Cardiac Electronic Devices Intechopen



Pacing
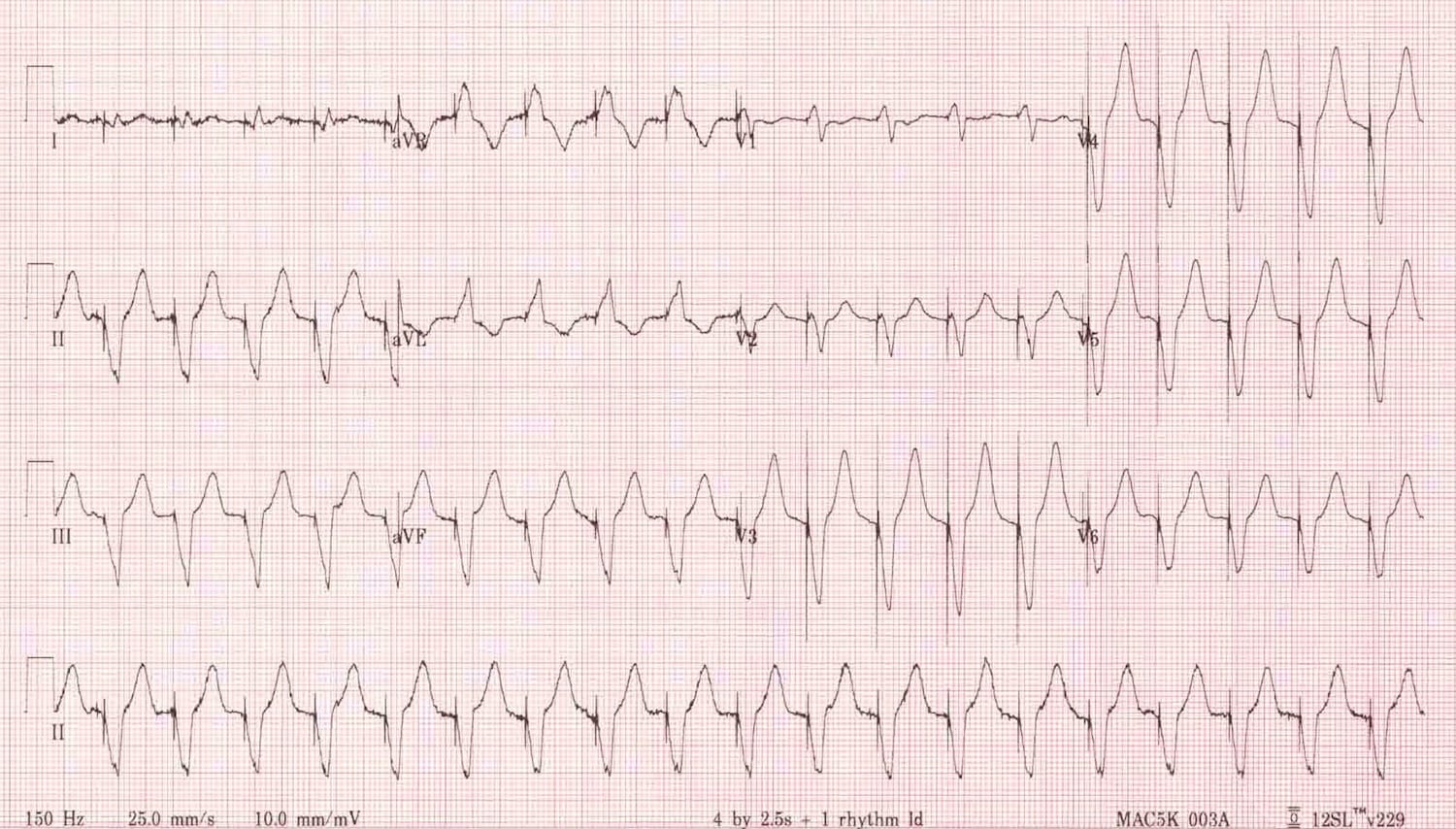



Pacemaker Basics Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog Extreme Bradycardia A Case Based Lesson In Pacing



Transcutaneous Pacing Tcp The Problem Of False Capture Ems 12 Lead




Ecg Module 3 Sinus Dysrrhythmias Flashcards Quizlet
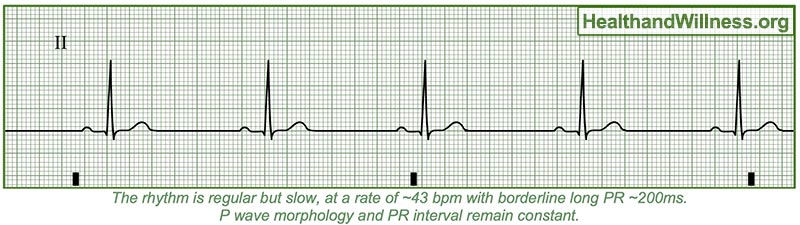



How To Read An Ekg Rhythm Strip Health And Willness
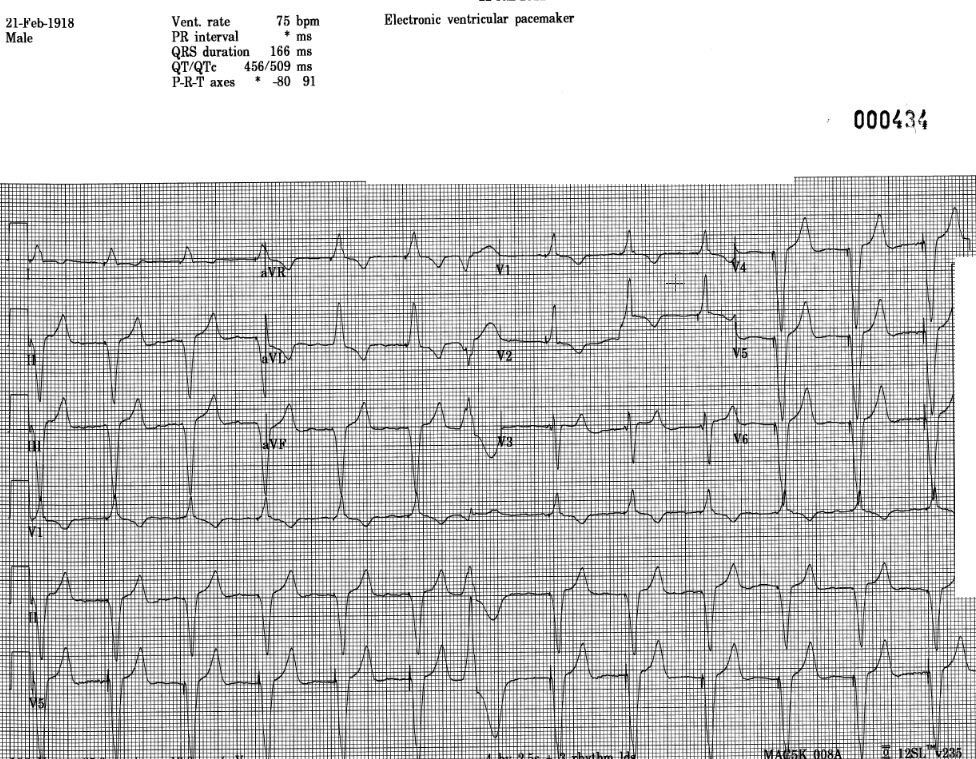



Pacemaker Ecg Guru Instructor Resources



1
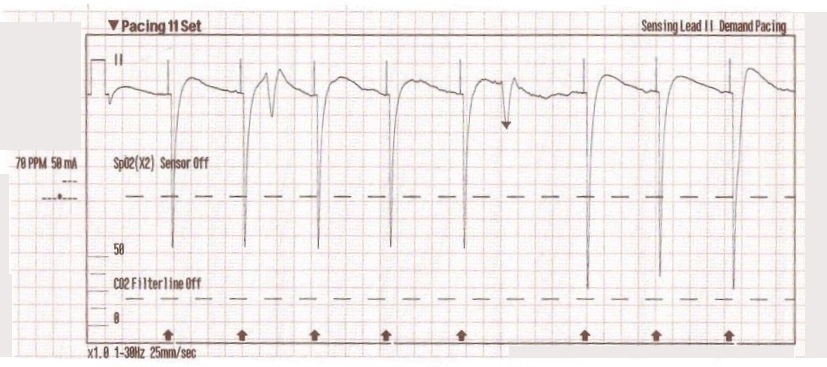



Transcutaneous Pacing Tcp With And Without Capture Acls Medical Training




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog Sinus Rhythm With A New Wide Complex Qrs



Utmc Utoledo Edu Depts Nursing Pdfs Advanced ekg refresher Pdf




Pacemakers And Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators Ppt Video Online Download




Pacemaker Learntheheart Com
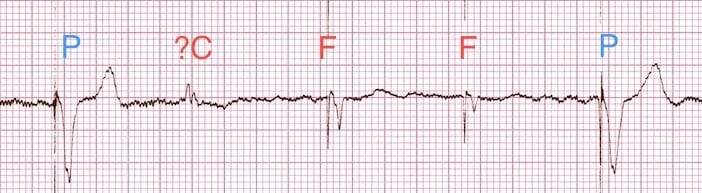



Pacemaker Rhythms Normal Patterns Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis
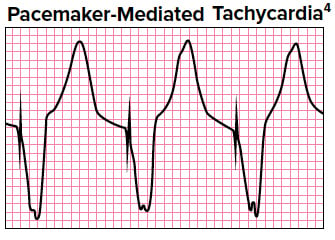



Pacemaker Basics For The Emergency Physician Emra




Pacemaker Review Rush Emergency Medicine




Electrocardiographic Troubleshooting Of Implanted Cardiac Electronic Devices Intechopen




Micro Ekg Mad Scientist Software




Electrophysiology Of The Heart Ecg Monitoring The Ecg



Www Ahajournals Org Doi Pdf 10 1161 01 Cir 57 1 98


コメント
コメントを投稿